How Refrigerators Changed the World
A World Without Refrigeration
Imagine a time when fresh produce wilted quickly, milk soured within hours, and meat was a rare luxury. This was the harsh reality before refrigerators. But with the advent of refrigeration, everything changed. Let’s embark on a journey through the history and science of refrigeration, and see how this humble invention transformed our lives.
From Ancient Ice Pits to Modern Marvels
Ancient Innovations: The First Steps in Food Preservation
- Egyptian Ice Pits (3500 BC): Early Egyptians used ice harvested from winter to cool their food. They stored it in underground pits lined with straw and mud, showcasing an early attempt at refrigeration.
- Persian Yakhchals (6th Century BC): In ancient Persia, Yakhchals were sophisticated ice houses that used thick mud walls, windcatchers, and qanats to store ice and keep food cool in desert conditions.
The Birth of Mechanical Refrigeration
John Gorrie’s Groundbreaking Air Conditioning (1851)
- A New Approach: Dr. John Gorrie developed an early air conditioning system using compressed air to cool hospital rooms, marking the first step toward modern air conditioning.
James Harrison and the Ice Revolution (1854)
- Commercial Ice Making: James Harrison invented the first successful ice-making machine, revolutionizing food preservation and long-distance meat transportation.
 The Rise of Home Refrigeration
The Rise of Home Refrigeration
Fred W. Wolf’s Home Electric Refrigerator (1913)
- A New Household Essential: Fred W. Wolf created the first home electric refrigerator, paving the way for domestic cooling.
Frigidaire and the Self-Contained Refrigerator (1923)
- A Sleek Solution: Frigidaire introduced the self-contained refrigerator, integrating the compressor within the cabinet for a more compact and user-friendly design.
The Efficiency Era: Advancements in Cooling Technology
The Freon Revolution (1930)
- Safer Refrigerants: The introduction of Freon, a non-toxic refrigerant, marked a turning point in refrigerator safety and efficiency.
The Dawn of Home Freezers (1940)
- Freezing for the Future: The addition of home freezers revolutionized food storage, allowing for longer preservation and convenience.
1950s – 1970s: Design and Efficiency Upgrades
- Sleeker Designs: Post-WWII innovations led to more attractive, energy-efficient refrigerators with features like automatic defrosting and adjustable temperature controls.
Modern Innovations: Refrigeration in the Digital Age
1980s – Present: Sustainability and Smart Technology
- Going Green: Modern refrigerators use natural refrigerants and inverter compressors to improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Smart Features: Wi-Fi connectivity, touchscreens, and internal cameras in smart refrigerators offer advanced features like remote monitoring and recipe suggestions.
How Refrigerators Work: The Science Behind the Chill
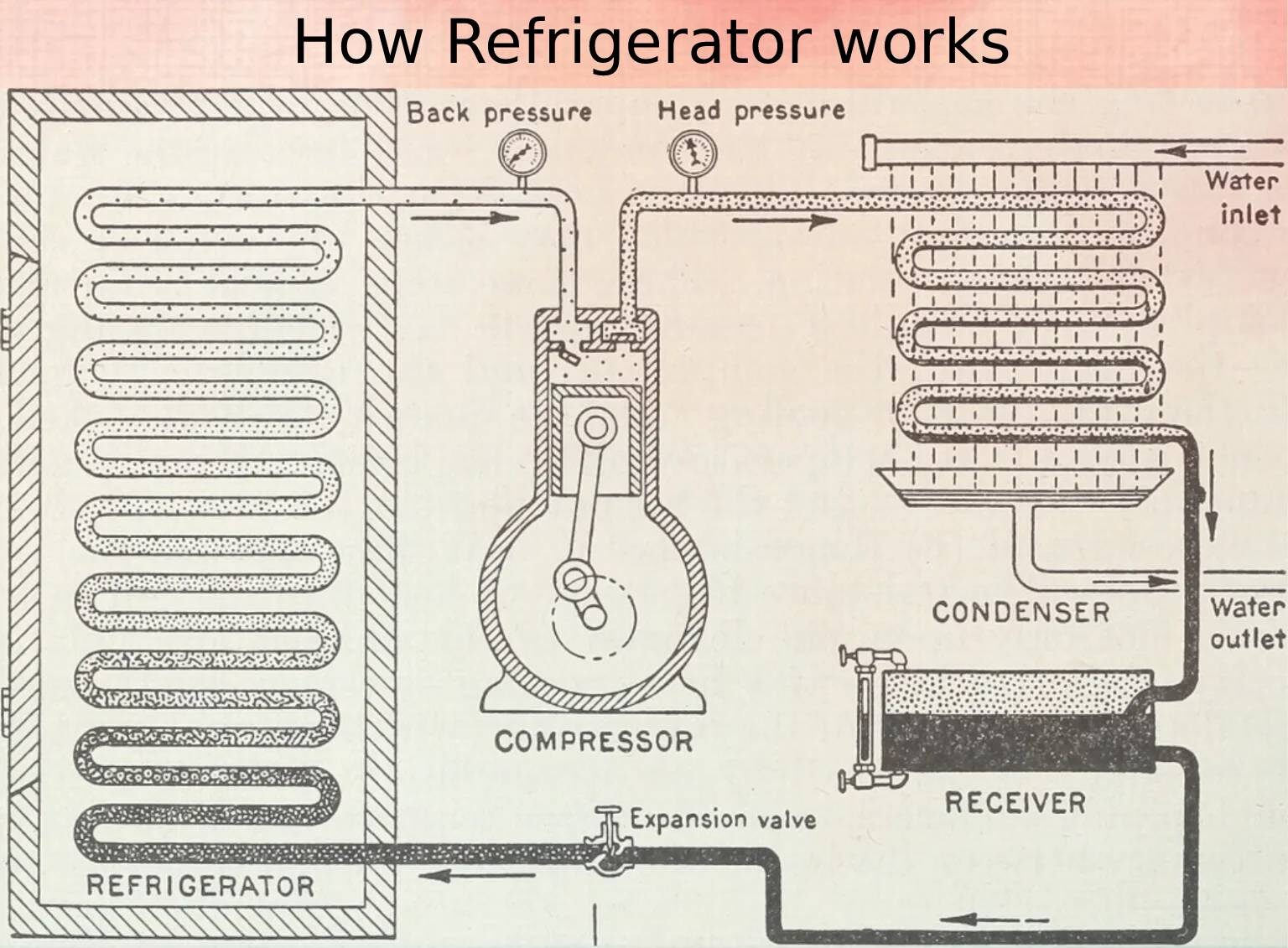
The Vapor-Compression Cycle: A Simple Breakdown
- Compression: Refrigerant gas is compressed, increasing its pressure and temperature.
- Condensation: The gas releases heat in the condenser coil and turns into a liquid.
- Expansion: The liquid passes through an expansion valve, cooling and turning into a gas.
- Evaporation: The gas absorbs heat inside the fridge and returns to the compressor to start the cycle again.
Choosing Refrigerants: From Harmful to Eco-Friendly
- Old vs. New: From CFCs and HCFCs to HFCs and natural refrigerants like ammonia and CO2, the choice of refrigerant has evolved to address environmental concerns.
Impact on Society: How Refrigeration Transformed the World
Food and Health
- Extended Freshness: Refrigeration has reduced food spoilage, expanded diets, and improved public health by preventing foodborne illnesses.
Economic and Social Changes
- Global Food Chain: Refrigeration enabled long-distance food transport and the rise of supermarkets, changing how and where we shop.
- Family Dynamics: With preserved foods, meal preparation time decreased, influencing family life and increasing workforce participation.
Environmental Considerations
- Mixed Legacy: While refrigeration has improved food access, early refrigerants harmed the environment. Modern innovations focus on sustainability and energy efficiency.
Beyond the Kitchen
Medicine and Industry
- Medical Advances: Refrigeration is vital for storing vaccines and medicines, advancing global health.
- Industrial Uses: Cooling systems are crucial in various industries, supporting technological innovation and manufacturing.
The Future of Refrigeration
 Innovations on the Horizon
Innovations on the Horizon
- Smart Tech and Sustainability: Future refrigerators may include AI-driven features, advanced sensors, and even better energy efficiency, continuing to evolve with technological advancements.
Appreciating the Cool Legacy
The refrigerator has come a long way from its primitive beginnings. It has not only changed how we store food but also impacted our health, economy, and environment. As we look forward to future innovations, we can appreciate how this cool invention has become an essential part of modern life.
Understanding Refrigeration and Refrigerators
1. What is a refrigerator and how does it work?
A refrigerator is an appliance that keeps food and drinks cold to prevent spoilage. It works using the vapor-compression cycle: refrigerant gas is compressed, cooled in the condenser coil, expanded, and evaporated inside the fridge to absorb heat. This cycle repeats continuously to maintain a low temperature inside.
2. How does a refrigerator keep food cold?
A refrigerator keeps food cold by removing heat from its interior. This is done through a cycle where refrigerant gas absorbs heat, turns into a liquid, releases heat outside, and then evaporates again inside to absorb more heat, maintaining a consistent cool temperature.
3. What are refrigerants and why are they important?
Refrigerants are substances used in refrigeration systems to transfer heat. Common refrigerants include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and natural options like ammonia and carbon dioxide. They are crucial for the efficiency and effectiveness of cooling systems.
4. How often should a refrigerator be cleaned?
To maintain efficiency and hygiene, you should clean the inside of your refrigerator every 1-2 months. This includes wiping down shelves, checking for expired food, and cleaning spills. Additionally, the condenser coils should be cleaned every 6-12 months to ensure optimal performance.
5. What are the benefits of a smart refrigerator?
Smart refrigerators come with features like Wi-Fi connectivity, touchscreens, internal cameras, and remote control via smartphone apps. They offer conveniences such as temperature monitoring, grocery list management, recipe suggestions, and alerts for maintenance issues.
6. How can I make my refrigerator more energy-efficient?
To enhance energy efficiency, keep the refrigerator at the recommended temperature (35-38°F or 1.7-3.3°C), ensure the door seals are airtight, clean the condenser coils regularly, and avoid overloading the fridge. Consider upgrading to a model with an Energy Star rating.
7. Why is my refrigerator making a loud noise?
A loud noise could indicate several issues, such as a malfunctioning compressor, loose condenser fan, or ice build-up. Check for loose parts or ice accumulation. If the noise persists, it might be necessary to contact a professional for repair.
8. How long does a refrigerator typically last?
On average, a refrigerator lasts about 10-20 years, depending on its brand, model, and maintenance. Regular upkeep and timely repairs can extend its lifespan.
9. What should I do if my refrigerator stops working?
If your refrigerator stops working, first check if it’s plugged in and the power is on. Ensure the thermostat is set correctly and check for any obstructions or ice build-up. If these steps don’t resolve the issue, consult a professional technician to diagnose and fix the problem.
10. How do I properly dispose of an old refrigerator?
Dispose of an old refrigerator according to local regulations. Many areas have recycling programs or special disposal services for large appliances. Ensure the refrigerant is properly removed by a certified technician before disposal to prevent environmental harm.
11. What temperature should a refrigerator be?
Your refrigerator should be set to 37°F (3°C) to keep food fresh and safe. This temperature helps slow the growth of bacteria while ensuring that food remains at its optimal quality.
12. How cold should a refrigerator be?
A refrigerator should ideally be kept at 37°F (3°C). This temperature is cold enough to preserve food effectively without freezing items inside.
13. How cold is a refrigerator?
Most refrigerators are set to maintain a temperature of around 37°F (3°C). This ensures that food stays fresh without freezing.
14. How many watts does a refrigerator use?
The average refrigerator uses between 100 to 800 watts, depending on its size and efficiency. Larger models and those with more features typically use more power.
15. How many amps does a refrigerator use?
Most refrigerators use between 1 to 5 amps. The exact amount depends on the model and its power rating. Larger and more advanced refrigerators may use more amps.
16. Who invented the refrigerator?
The modern refrigerator’s invention is credited to Jacob Perkins, who patented the first practical vapor-compression refrigeration system in 1834.
17. How long will food last in a refrigerator without power?
Food can generally remain safe in a refrigerator for about 4 hours without power, as long as the door is kept closed. After this period, the safety of the food can no longer be guaranteed.
18. How long do eggs last in the refrigerator?
Eggs can typically be stored in the refrigerator for 3 to 5 weeks. They should be kept in their original carton and placed in the coldest part of the fridge.
19. How much does a refrigerator weigh?
The weight of a refrigerator varies widely depending on its size and type, but most range from 150 to 400 pounds (68 to 181 kg).
20. What is a counter-depth refrigerator?
A counter-depth refrigerator is designed to align with your kitchen counters, offering a sleek, built-in look. It typically has a shallower depth compared to standard refrigerators, providing a more seamless appearance.
Top 10 Refrigerators of 2024
Here’s a look at the top ten refrigerators for 2024, showcasing their specifications and standout features to help you choose the best option for your needs:
1. Samsung Refrigerator RF28R7201SR
- Type: French Door
- Capacity: 28 cu. ft.
- Features:
- Family Hub™ with Wi-Fi connectivity
- Built-in cameras for interior viewing
- FlexZone™ Drawer with adjustable temperature settings
- Triple Cooling System
- Ice Maker and Water Dispenser
2. LG Refrigerator LFXS28968S
- Type: French Door
- Capacity: 28 cu. ft.
- Features:
- SmartThinQ™ technology for remote control and diagnostics
- InstaView™ Door-in-Door®
- Dual Ice Makers
- Fresh Air Filter with deodorizing
- LED Lighting
3. Whirlpool Refrigerator WRX735SDHZ
- Type: French Door
- Capacity: 25.2 cu. ft.
- Features:
- AccuFresh™ Dual Cooling System
- FreshFlow™ Air Filter
- Exterior Ice and Water Dispenser
- 3-Tier Freezer Drawer
- Adaptive Defrost
4. GE Profile Refrigerator PFE28KYNFS
- Type: French Door
- Capacity: 27.9 cu. ft.
- Features:
- Keurig® K-Cup® Brewing System
- TwinChill™ Evaporators
- Hands-free AutoFill Water Dispenser
- Advanced Temperature Management System
- LED Lighting
5. Bosch Refrigerator B36CL80ENS
- Type: Bottom-Freezer
- Capacity: 21 cu. ft.
- Features:
- EcoMode for energy savings
- Dual Evaporators
- MultiAirFlow™ System
- Interior LED Lighting
- NoFrost Technology
6. Frigidaire Refrigerator FPBS2777RF
- Type: Side-by-Side
- Capacity: 27.6 cu. ft.
- Features:
- PureSource Ultra® Water Filter
- Ice Maker with Fast Ice feature
- SpaceWise® Adjustable Glass Shelves
- Door Bins with Adjustable Dividers
- Bright LED Lighting
7. Maytag Refrigerator MFI2570FEZ
- Type: French Door
- Capacity: 25 cu. ft.
- Features:
- PowerCold® Feature
- Produce Preserver to extend freshness
- External Water and Ice Dispenser
- 10-Year Limited Parts Warranty
- LED Interior Lighting
8. KitchenAid Refrigerator KRFC300ESS
- Type: French Door
- Capacity: 20 cu. ft.
- Features:
- Preserva® Food Care System
- External Ice and Water Dispenser
- SatinGlide® Crispers
- LED Interior Lighting
- Adjustable Spill-Resistant Shelves
9. Hisense Refrigerator HRF266N6C
- Type: Side-by-Side
- Capacity: 25.5 cu. ft.
- Features:
- Adjustable Glass Shelves
- LED Lighting
- Ice Maker
- Multi-Air Flow System
- Electronic Temperature Control
10. Samsung Refrigerator RS27T5200SR
- Type: Side-by-Side
- Capacity: 27.4 cu. ft.
- Features:
- Ice Maker with Water Dispenser
- Twin Cooling Plus™ Technology
- LED Lighting
- Adjustable Door Bins
- Digital Touch Controls
These top refrigerators offer a variety of styles and features to meet different needs, from advanced smart technology to efficient cooling systems.

